Tactical Medicine: Everything You Need to Know
Content
- What is Tactical Medicine?
- History and Development of Tactical Medicine
- Basic Principles and Tasks of Tactical Medicine
- Provision of First Aid
- Effective Resource and Personnel Management
- Use of Advanced Medical Technologies
- Training and Preparation of Medical Personnel
- Stages of Providing Assistance in Tactical Medicine
- Assistance in the "Red Zone"
- Assistance in the "Yellow Zone"
- Assistance in the "Green Zone"
- Algorithms for Providing Assistance
- Tactical Medicine in Ukraine
One of the key reasons for the urgent need for first aid in conditions of armed aggression is the inability to immediately hospitalize wounded individuals. During conflicts, reaching hospitals or medical facilities can be complicated or delayed. Therefore, providing effective assistance on-site becomes crucial for reducing traumatic consequences and supporting vital bodily functions.
What is Tactical Medicine?

Tactical medicine involves providing medical assistance during military actions. The implementation of this training for every military personnel in Western armies has led to remarkable results, reducing injury-related losses in the U.S. military to historic lows. Tactical medicine considers the specificity of the location and circumstances where aid is provided during combat, differing from conventional hospitals, medical vehicles, or even city sidewalks.
The swift initiation of pre-medical assistance in combat conditions is identified as a key factor significantly increasing the chances of survival and recovery for the wounded. Hence, the concept of the "golden hour" exists—the first hour after sustaining an injury when qualified medical assistance must commence.
Every modern army fighter, in addition to weapon proficiency, physical and tactical training, possesses a high level of skills in providing medical aid in combat conditions. Fighters lacking knowledge in tactical medicine pose a threat to themselves and their comrades.
The Tactical Medicine section is dedicated to teaching fundamental skills for independent and mutual medical assistance in combat conditions. Its materials will be valuable in preparing military personnel for providing first aid and treatment in areas of gunfire and shelter.
History and Development of Tactical Medicine
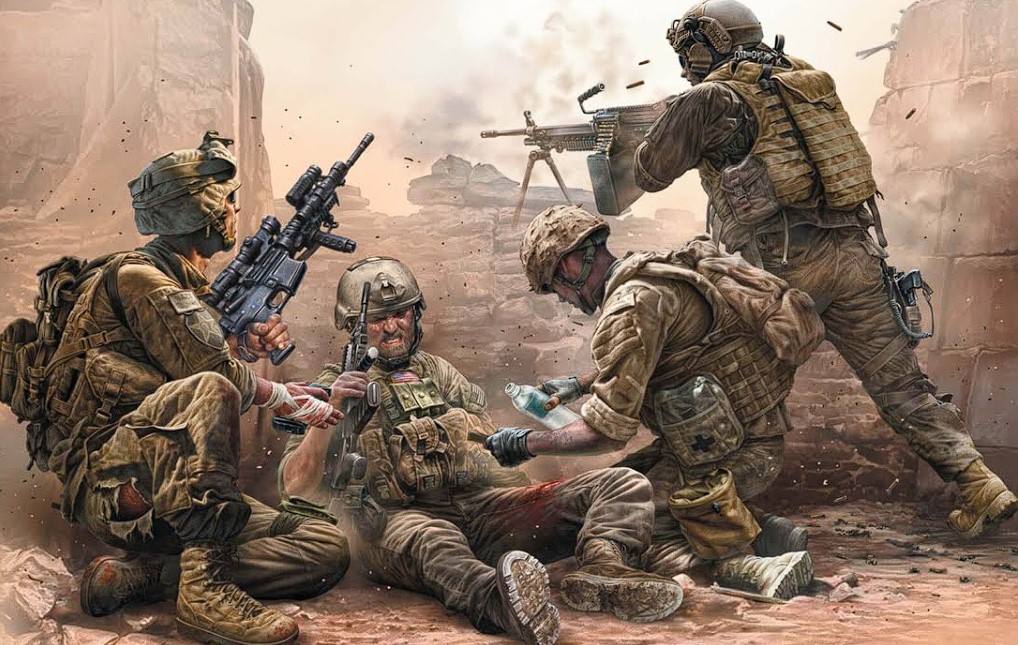

In the early 1990s, the U.S. and the U.K. conducted research to develop standards for providing pre-hospital care in combat conditions. For example, in 1993, the U.S. Special Operations Command funded a two-year study to improve medical aid to the wounded on the battlefield. This study led to the creation of the first edition of Tactical Combat Casualty Care (TCCC) recommendations. Simultaneously, in the U.K., a parallel and independent study was conducted, resulting in a course developed for the Special Air Service and Special Boat Service based on ATLS.
In 1996, the journal "Military Medicine" published an article titled "Tactical Combat Casualty Care in Special Operations," detailing the first American pre-hospital care guidelines known as Tactical Combat Casualty Care (TCCC or TC3), based on the aforementioned research. These guidelines are annually reviewed by a committee comprising military physicians and paramedics from various specialties and branches. Currently, most NATO armies use similar standards.
Basic Principles and Tasks of Tactical Medicine
The primary causes of death in 80-90% of cases among the wounded are significant blood loss and shock. The conditions of modern armed conflicts limit the possibilities of providing pre-medical assistance on the front lines, leading to critical timeframes for implementing appropriate medical measures. Death in such situations can occur within seconds to one hour.
Tactical medicine is based on the principles of rapid response, treatment priorities, and mobility. The main task is to prevent death and minimize traumatic consequences. This is achieved by providing quick assistance on the front lines, efficiently evacuating the wounded, and training soldiers to administer first aid in combat conditions.
Provision of First Aid
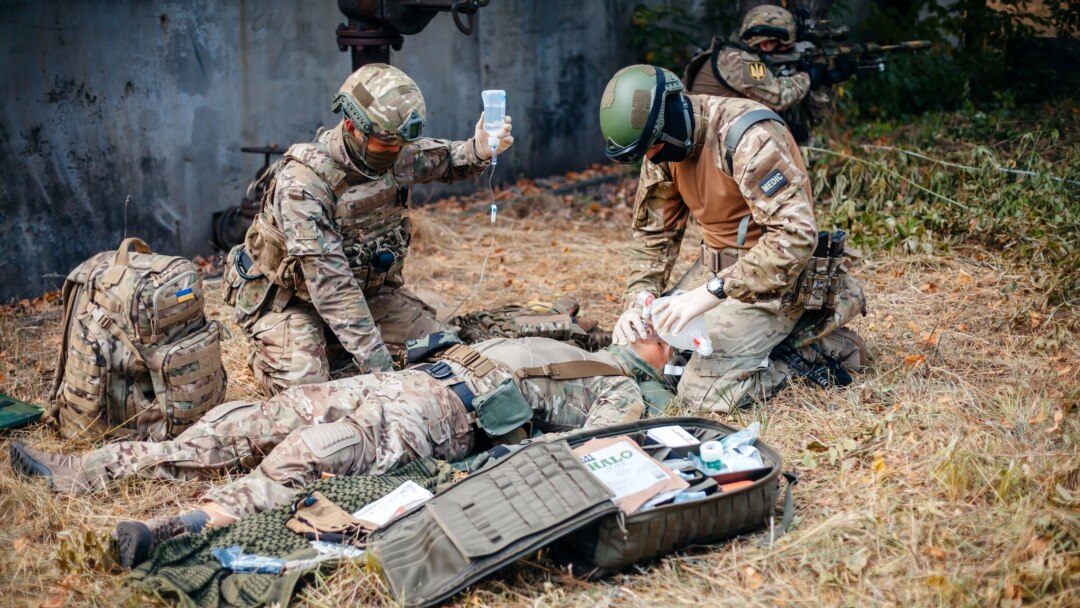

Providing first aid involves a swift and competent response to urgent medical situations. The main aspects of this process include providing immediate assistance to the injured, effective control of bleeding and other dangerous conditions, and rapid transportation of the casualties to medical facilities for further treatment. An important component is educating a wide range of individuals in basic first aid principles and skills to ensure safety and health in emergency situations.
Effective Resource and Personnel Management
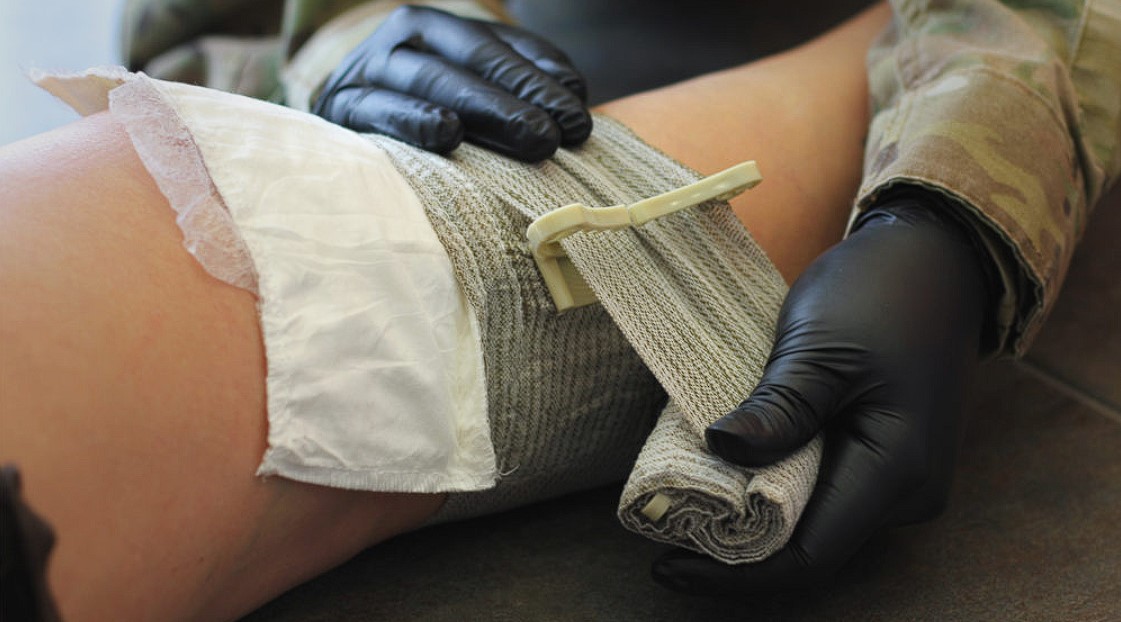
Effective resource and personnel management in tactical medicine involve the rational distribution of equipment and medical materials, strategic planning for optimal use of limited resources, and qualified deployment of personnel for an effective response to urgent medical situations.
This includes training and coordinating medical personnel for the efficient conduct of operations in combat conditions or other emergency circumstances.
Use of Advanced Medical Technologies
The use of advanced medical technologies in tactical medicine opens up new possibilities for providing high-quality medical assistance in combat and extreme conditions.
This includes the use of cutting-edge medical devices for rapid diagnosis and monitoring, telemedicine for remote consultation and decision support, as well as high-precision information processing technologies to enhance the coordination of medical personnel actions.
Innovations in medical technology contribute to the increased efficiency and effectiveness of tactical medicine, ensuring a quick and accurate response to complex situations and saving more lives.
Training and Preparation of Medical Personnel
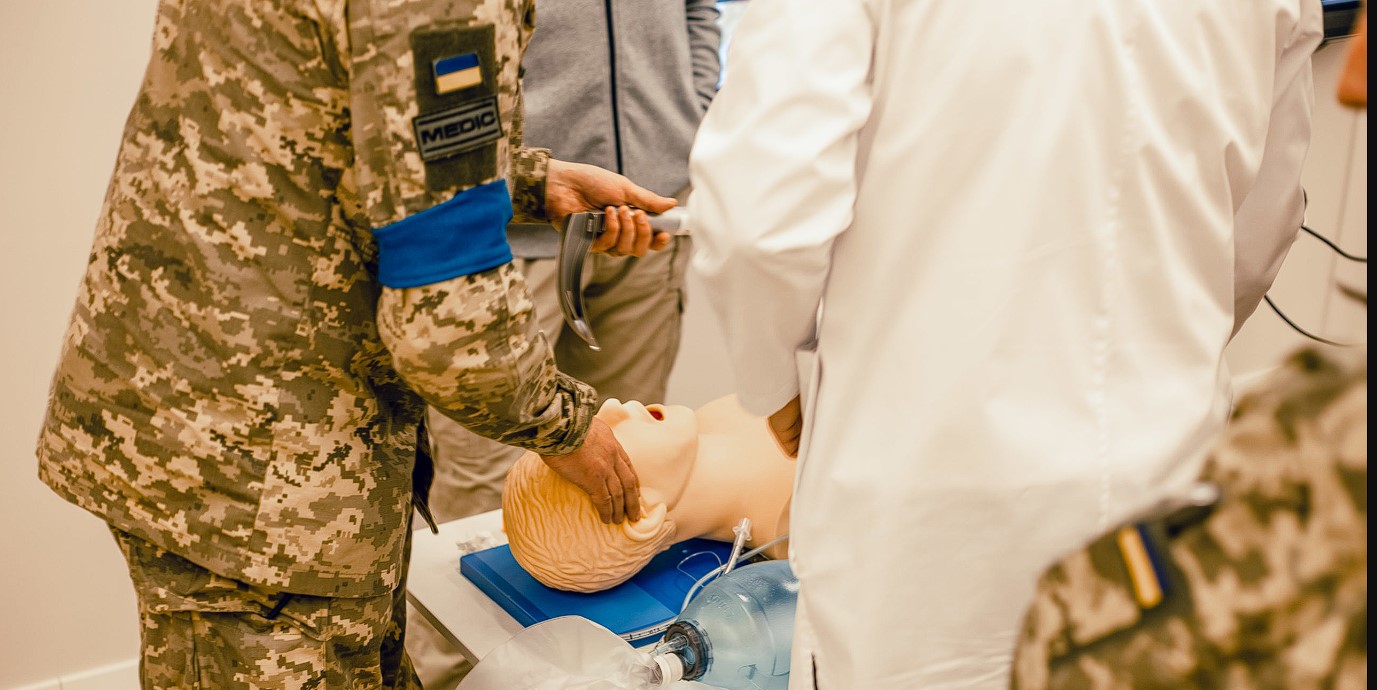
Training and preparation of tactical medical personnel play a crucial role in ensuring effective medical assistance in combat and emergency situations. This process includes:
- Specialized training: Medical personnel acquire specialized skills and knowledge tailored to the specific challenges of tactical medicine, including severe injuries, evacuation, and working in conditions of limited accessibility.
- Combat scenario training: Training is conducted with realistic scenarios simulating combat conditions, allowing medical personnel to test their skills in real situations.
- Equipment and gear: Medical personnel learn to effectively use specialized medical equipment and advanced gear for a quick and accurate response to injuries and emergency conditions.
- Team coordination: Training includes elements of teamwork to ensure effective collaboration among different links in the chain of medical assistance.
- Self-aid training: Medical personnel learn self-aid methods in stressful conditions and limited resources, which can be crucial in combat situations.
Such training helps ensure a high level of readiness for medical personnel and enhances their ability to intervene effectively in the most challenging conditions.
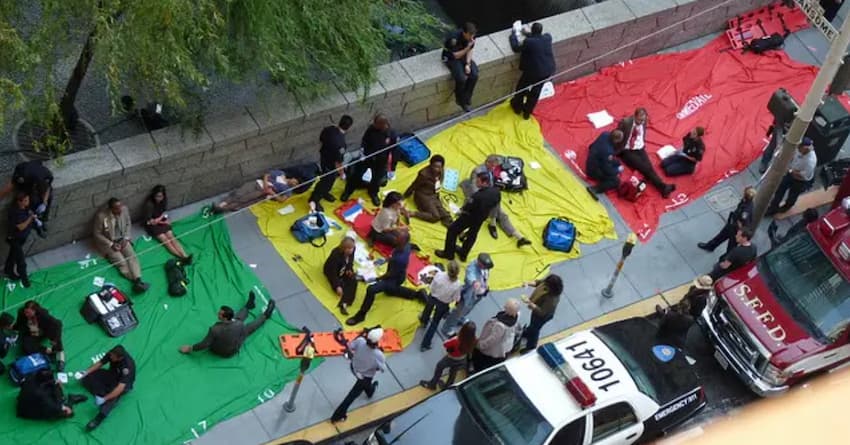
Stages of Providing Assistance in Tactical Medicine
There are two main places where pre-medical assistance can be provided during military operations:
- Directly in the line of fire;
- In a covered area.
The process of providing assistance to the wounded in military field conditions is divided into three stages.
The first stage involves providing assistance in the "red zone" (Care Under Fire), where the rescuer is under enemy fire, significantly limiting the amount of aid they can provide. The primary focus is on using tourniquets and promptly moving the casualties to a safe location.
Assistance in the "Red Zone"

The conditions of combat make being a rescuer a secondary mission. The main function is to fulfill the primary mission. The main priorities on the battlefield remain engaging in fire response, repelling enemies, and achieving the following goals when assisting the wounded in the line of fire:
- Executing the combat mission;
- Preventing an increase in casualties;
- Preserving the lives of the wounded.
After completing the stage of providing medical assistance in the line of fire, medical assistance takes place in the "covered zone."
Assistance in the "Yellow Zone"

The second stage of medical assistance in military field conditions, taking place in the "yellow zone," begins only after the rescuer and the wounded are no longer under direct enemy fire. At this stage, there is more time for providing aid, but medical equipment and materials are limited to what was available on the battlefield from the rescuer or individual soldiers. The procedures for providing medical assistance at this stage include:
- Assessing the condition of the injured according to the C-A-B-C rule (critical bleeding - airway - breathing - circulation) and providing necessary assistance.
- Checking for the presence of dangerous bleeding.
- Taking measures to restore the patency of the airways, including inserting a nasopharyngeal airway if necessary.
- Treating open chest injuries and decompressing tension pneumothorax.
- Checking the condition of the tourniquet if previously applied and controlling bleeding.
- Examining for minor bleeding.
- Checking for untreated wounds on the limbs that may be life-threatening and treating them.
- Continuing the treatment of other injuries, including applying splints for fractures, dressing other wounds, burns, etc.
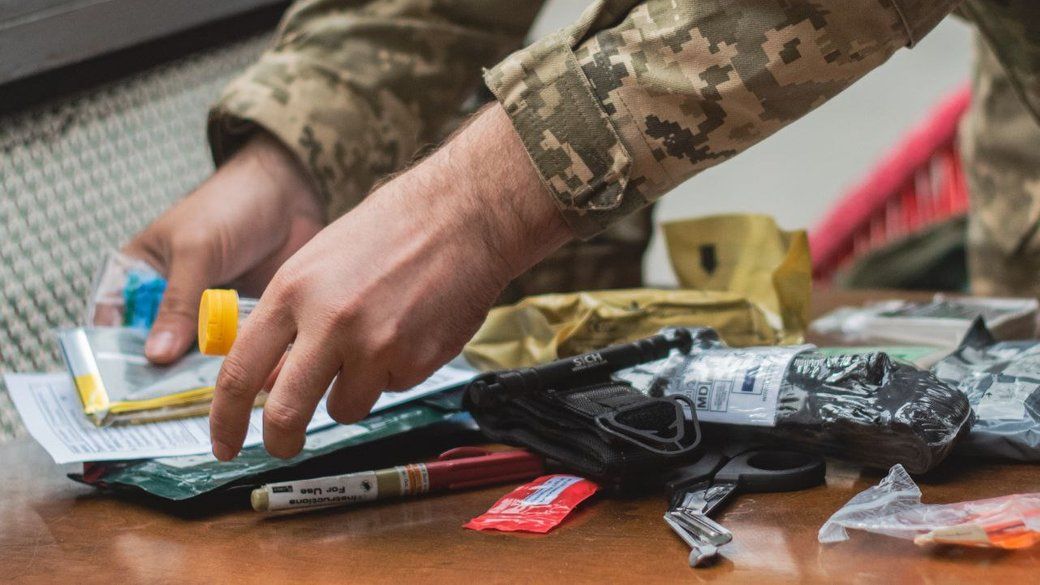
- Administering painkillers and antibiotics from the individual first aid kit (IFAK) and using it for the medical care of the wounded.
- Taking measures to prevent the development of or provide assistance in the case of shock.
- Reporting information about the medical situation to the unit commander and calling for a military paramedic if necessary.
- Monitoring the condition of the injured, including regular checks of consciousness and breathing.
- Preparing the wounded for evacuation if necessary and keeping records of the medical procedures performed.
Assistance in the "Green Zone"
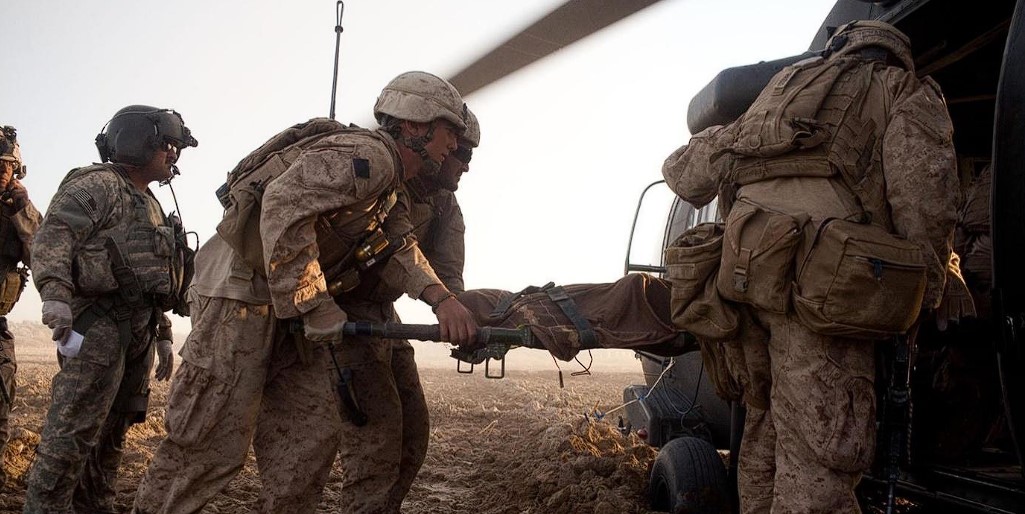

The third stage is the phase of providing assistance during tactical evacuation.
During evacuation, assistance is provided before the casualty reaches a collection point or a medical facility.
There are two types of evacuation: non-medical and medical.
- Non-medical evacuation involves moving the casualty using non-medical transport or aerial means. During this process, the rescuer may remain with the casualty to provide assistance during transportation.
- Medical evacuation includes evacuating casualties using specialized medical vehicles or a medical aircraft. Medical personnel are present on medical transport vehicles, which can be either ground or airborne, to provide assistance to casualties during evacuation.
In both cases, assistance is provided according to the C-A-B-C protocol.
Casualties should be promptly moved to the next level of medical care, as otherwise valuable resources will be spent on maintaining patients, complicating the provision of assistance to other casualties.
Algorithms for Providing Assistance
In tactical medicine, an algorithmic approach is used for providing assistance. Combat medics receive training on the sequence of aid provision, starting with the most critical injuries, such as massive bleeding, predominantly arterial.
The next stage involves checking the airway and ensuring the casualty's ability to breathe. Following these steps, a tactical medic must assess the casualty, ensure the absence of other injuries such as pneumothorax, fractures, and mechanical injuries, and identify other wounds and contusions.
The final stage is avoiding hypothermia, which may arise due to significant blood loss, disrupting the body's ability to regulate temperature independently.
The most widely used algorithm for providing pre-medical assistance in combat conditions is MARCH, where each letter represents a specific action and the sequence of execution:
- M — Massive Bleedings
- A — Airway
- R — Respiration
- C — Circulation
- H — Hypothermia
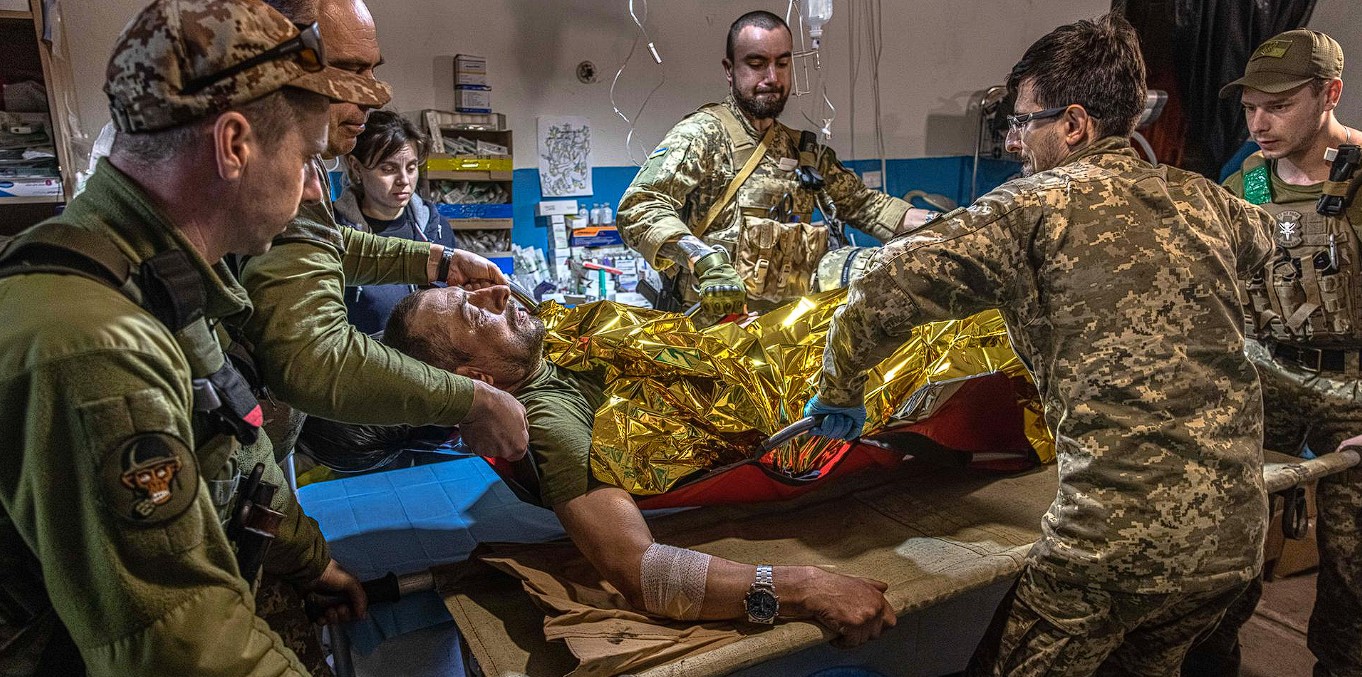
Tactical Medicine in Ukraine
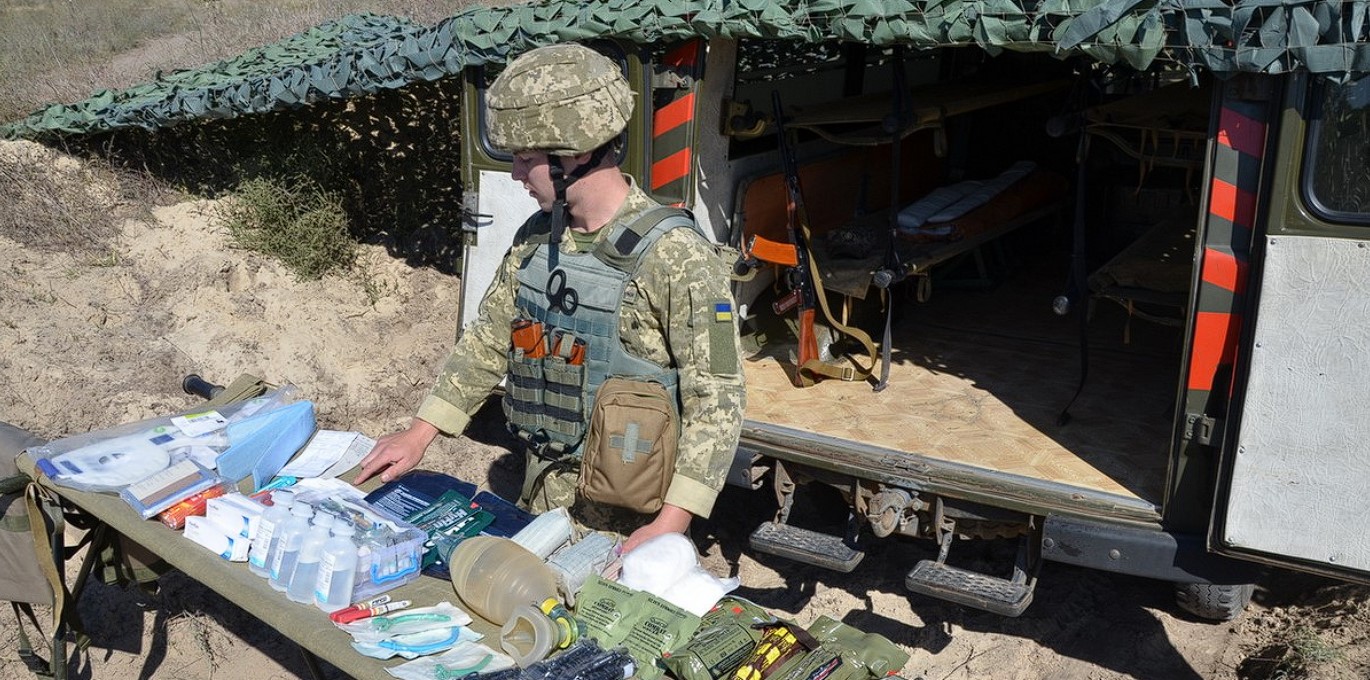

In Ukraine, the development of tactical medicine holds particular significance due to the ongoing military conflict in the eastern part of the country. Since the beginning of 2014, Ukraine has been facing challenges related to an armed conflict, creating the need for a high level of preparedness among medical personnel to provide assistance to the wounded on the battlefield.
The importance of tactical medicine in Ukraine lies in its crucial role in ensuring effective medical aid to the injured in combat conditions. Knowledge and skills in tactical medicine are critical for saving lives and reducing the impact of injuries on participants in military conflicts.
The development of tactical medicine in Ukraine involves training medical personnel participating in military operations using modern methods and strategies, such as Tactical Combat Casualty Care (TCCC). These programs provide practical skills and knowledge for the efficient response to injuries and the provision of aid on the battlefield.
Furthermore, tactical medicine becomes an essential component of training not only for military personnel but also for emergency medical doctors and other healthcare professionals. It can also be valuable in the public sector for preparing personnel who may encounter extreme situations.
Therefore, the development of tactical medicine in Ukraine is seen not only as essential for the military sphere but also in the context of raising the overall readiness of medical personnel to provide assistance in emergency situations.