Tactical Field Medic Kit
Content
- Who is a Combat Medic?
- Components of the Tactical Medic Kit
- Dressing Materials
- Hemorrhage Control Agents
- Disinfection Agents
- Painkillers
- Pneumothorax
- Airway Management Tools
- Additional Medical Tools
- Importance of the First Aid Kit in Tactical Medicine

The conditions on the battlefield pose a high-risk environment for the lives and health of individuals involved in military actions. Members of the armed forces and participants in combat operations often face the need for immediate and operative medical assistance. This assistance is provided by combat medics and military surgeons.
To address the tasks at hand, they use both time-tested methods and innovative, highly effective developments. Depending on the nature of the injury be it deep gunshot wounds, bleeding, respiratory arrest, and so on the medic chooses the optimal method of providing assistance.
Special attention is given to the composition of the paramedic's kit, which must be equipped with tools aimed at quickly and effectively providing first aid in combat conditions.
Who is a Combat Medic?
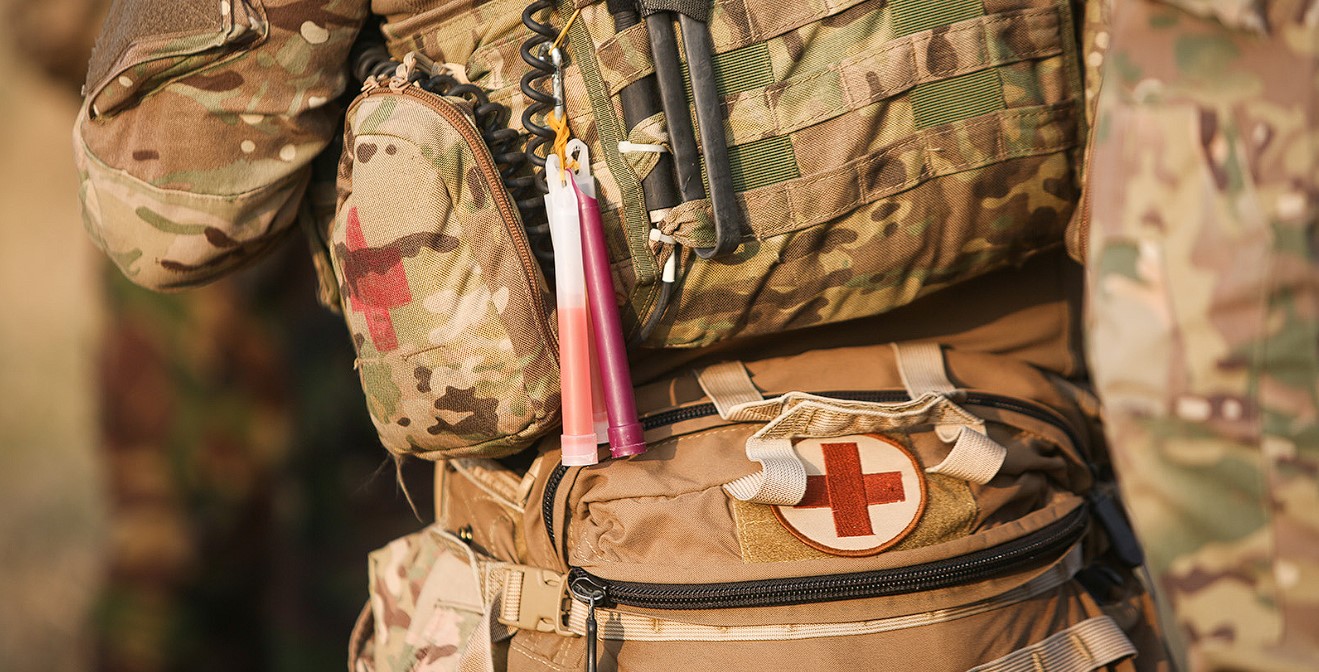
A combat medic is responsible for providing urgent medical assistance at the site of injury in combat or training environments. They are also tasked with offering primary care, health protection, and evacuation from the site of injury or illness. Additionally, they may take on the responsibility of creating, supervising, and implementing long-term care plans for patients in collaboration with a doctor or in their absence. Combat medics can work in hospitals and clinics, performing additional duties such as handling medical and laboratory equipment, conducting procedures, or providing assistance during their implementation.
On the front lines, combat medics work directly by providing pre-medical assistance to the wounded, sorting them, and coordinating the evacuation process.
Components of the Tactical Medic Kit
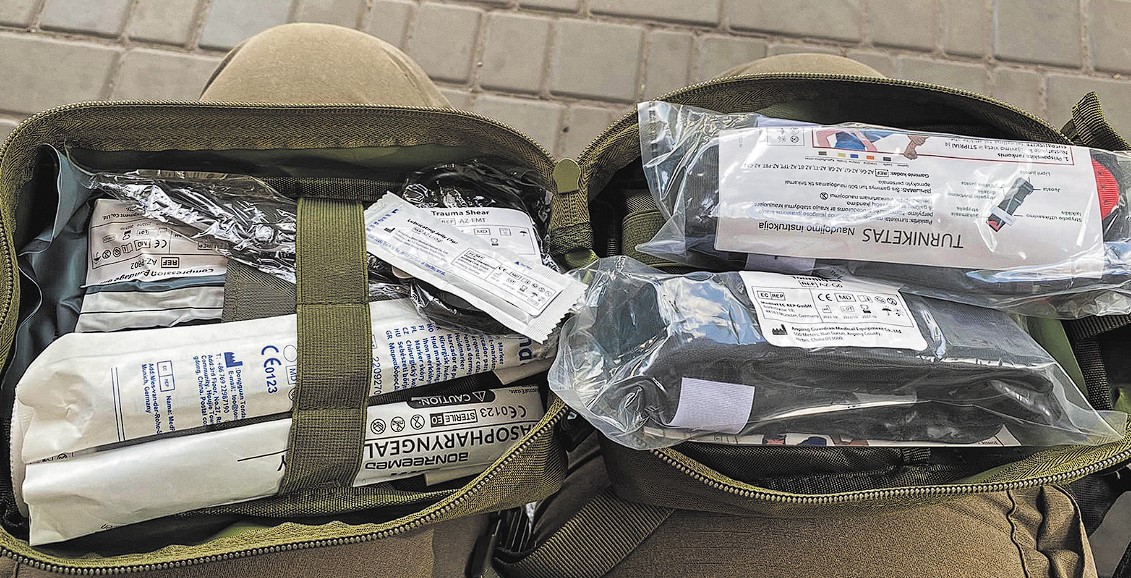
A military medical kit should include all necessary medical supplies and equipment required for providing first aid in military operations or military training. The military kit must contain effective tools to stop bleeding, treat injuries and other traumas, as well as medications for rapid health recovery and maintaining the well-being of military personnel.
An essential element of the military medical kit is also the presence of means for degassing and protection from chemical or biological threats that may arise on the battlefield. Additionally, the kit should contain basic medical instruments to assist in simple procedures and wound care.
It is also important to consider the specificity of military tasks when forming the medical kit, including the possibility of long periods of self-sufficiency and operational conditions in challenging circumstances. This is a crucial aspect for military medical personnel to respond effectively and promptly to any medical incidents in a military environment.
Dressing Materials
Sterile bandages, gauze, cotton, and adhesive plaster with antiseptic are used in various purulent, infectious, and bleeding skin and soft tissue injuries that require regular dressing. Due to this, dressing materials are quickly depleted, so they should constitute a significant part of the paramedic's medical kit.
Hemorrhage Control Agents
To stop bleeding of various localization and origin, military surgeons need to have at their disposal agents among which they could make an immediate and correct choice.
Bandages, napkins, and other agents with hemostatics contribute to the activation of the blood clotting process, making them an effective solution for stopping critical bleeding.
A tourniquet allows, with minimal time loss, to constrict a damaged vessel, providing enough time for transporting the casualty to the operating room.
Disinfection Agents
For providing qualified surgical assistance, adherence to aseptic and antiseptic principles is mandatory. Therefore, the use of special solutions for rinsing and disinfecting wounds and the surrounding skin area helps prevent blood infection and other complications.
Painkillers
Any injuries, burns, and severe impacts during combat operations are accompanied by significant discomfort, which may intensify when attempting to move the casualty. Having analgesics in the paramedic's kit allows for an effective resolution of this issue.
Pneumothorax
This category includes occlusive ventilated dressings and decompression needles used by military surgeons for treating pneumothorax during pre-hospital care and penetrating chest injuries.
Airway Management Tools
In situations of prolonged respiratory arrest, tracheal intubation is performed, making it important for a military surgeon to have a field laryngoscope in their arsenal. In cases of short-term respiratory disturbance, the use of a laryngeal mask, oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal airways is essential.
Additional Medical Tools
Additional medical tools that may be in the arsenal of a military doctor usually depend on their specialization, specific location requirements, and the type of military operations. However, here are a few general categories of additional medical tools:
- Hemostatics: powder hemostatics used for quickly stopping bleeding and improving blood clotting. Gel Hemostatics provide effective control of bleeding in case of injuries.
- Infusion and Injection Systems: rapid infusion systems allow for the quick administration of fluids and medications. Auto-injectable systems can be used for administering dosed injections in situations where time is critical
- Equipment for detection and combatting chemical threats: toxic substance detectors help detect the presence of chemical threats. Special protective suits and masks provide protection against toxic substances.
- Specialized instruments for tracheal intubation: field laryngoscopes used for tracheal intubation in the absence of stationary equipment.
- Systems for resuscitation and life support: mobile defibrillators aid in restoring heart rhythm in emergency situations. Automated Respirators used for artificial lung ventilation.
These are just a few examples. Additional medical tools for a military doctor can encompass a wide range of equipment aimed at maximizing medical care and management in combat conditions.
Importance of the First Aid Kit in Tactical Medicine
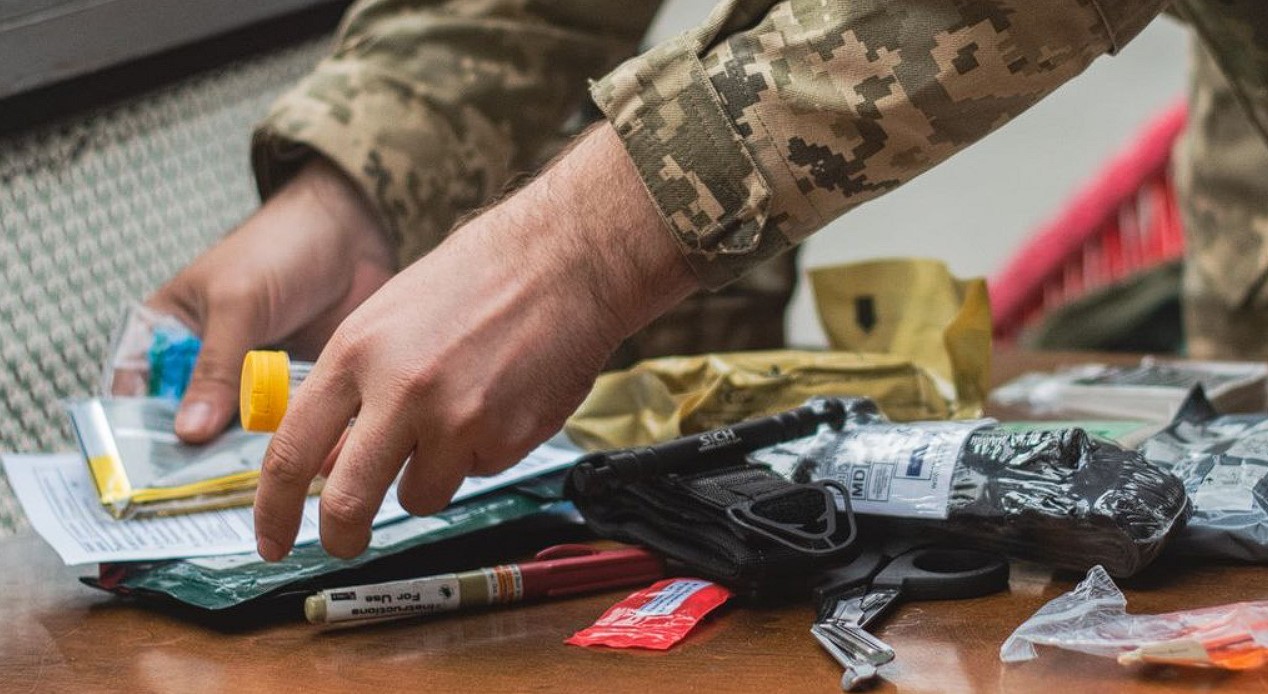

The first aid kit in tactical medicine plays a crucial role in providing prompt and effective medical assistance in combat conditions. Its importance is determined by several key aspects:
- Rapid response to injuries: The first aid kit enables quick first aid in the case of injuries and wounds, reducing response time and improving chances of saving lives or preventing further complications.
- Mobility and accessibility: Due to its compactness and portability, the first aid kit can be easily carried into the battlefield, providing the opportunity for medical service over a large area where quick access to stationary medical assistance may not be possible.
- Adaptability to combat conditions: The first aid kit is designed to operate in conditions of military conflicts, where chemical, biological, or radiation threats may be present. Its components must be adapted to protect against such dangers.
- Comprehensive tool set: The first aid kit contains various medical materials, such as dressing materials, antiseptics, hemostatics, intubation tools, bleeding control measures, and other items, allowing for handling diverse medical situations.
- Training and preparation: The first aid kit is an integral part of training and preparing medical personnel. It helps doctors and specialists refine their skills and practice protocols for providing assistance.
The first aid kit in tactical medicine is an important tool for medical care in military settings, providing rapid response, mobility, adaptability and comprehensiveness in dealing with different situations.
