Pill pack: what medicines a soldier needs in his individual first aid kit
Content
- Pill pack warehouse for the military
- Paracetamol 500 mg tablets
- Meloxicam 15 mg tablets
- Gatifloxacin 400 mg tablets
- What not to put in the Pill pack
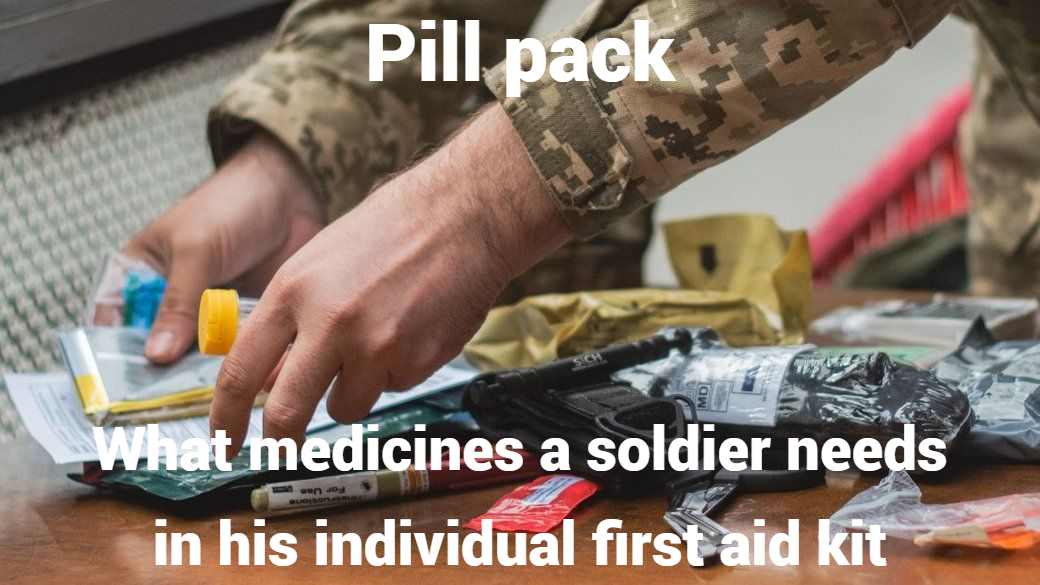
A military first aid kit is a critical tool for providing first aid in combat situations. It was developed based on the standardised recommendations of the TCCS committee, which is part of the US Department of Defence's Unified Trauma Care System. This kit is an indispensable element of a soldier's equipment and can save lives in combat situations.
Pill pack warehouse for the military
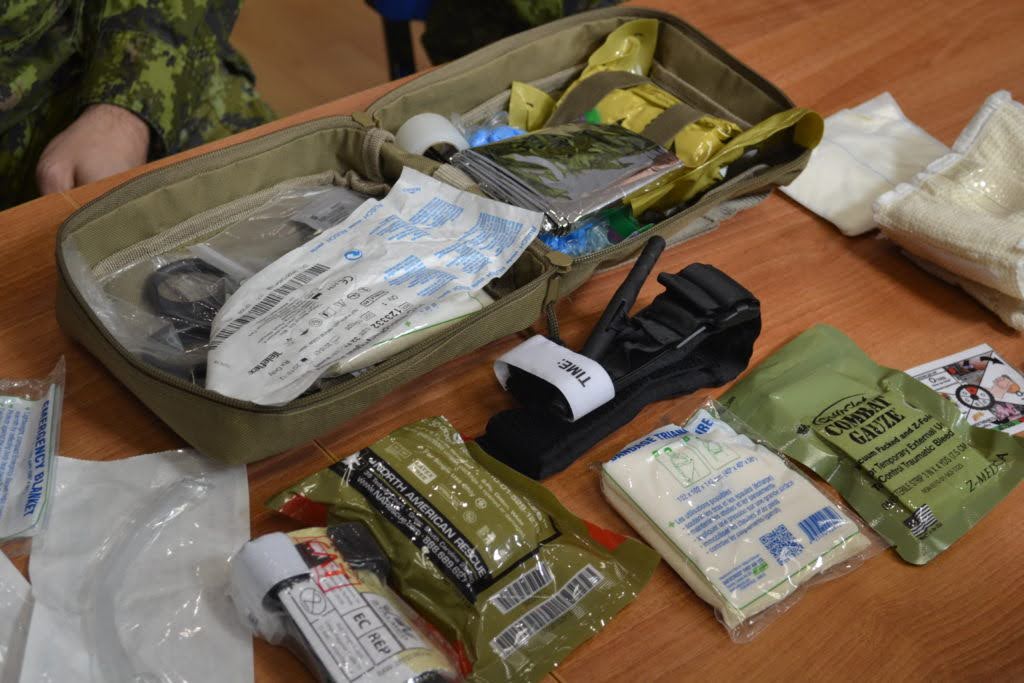

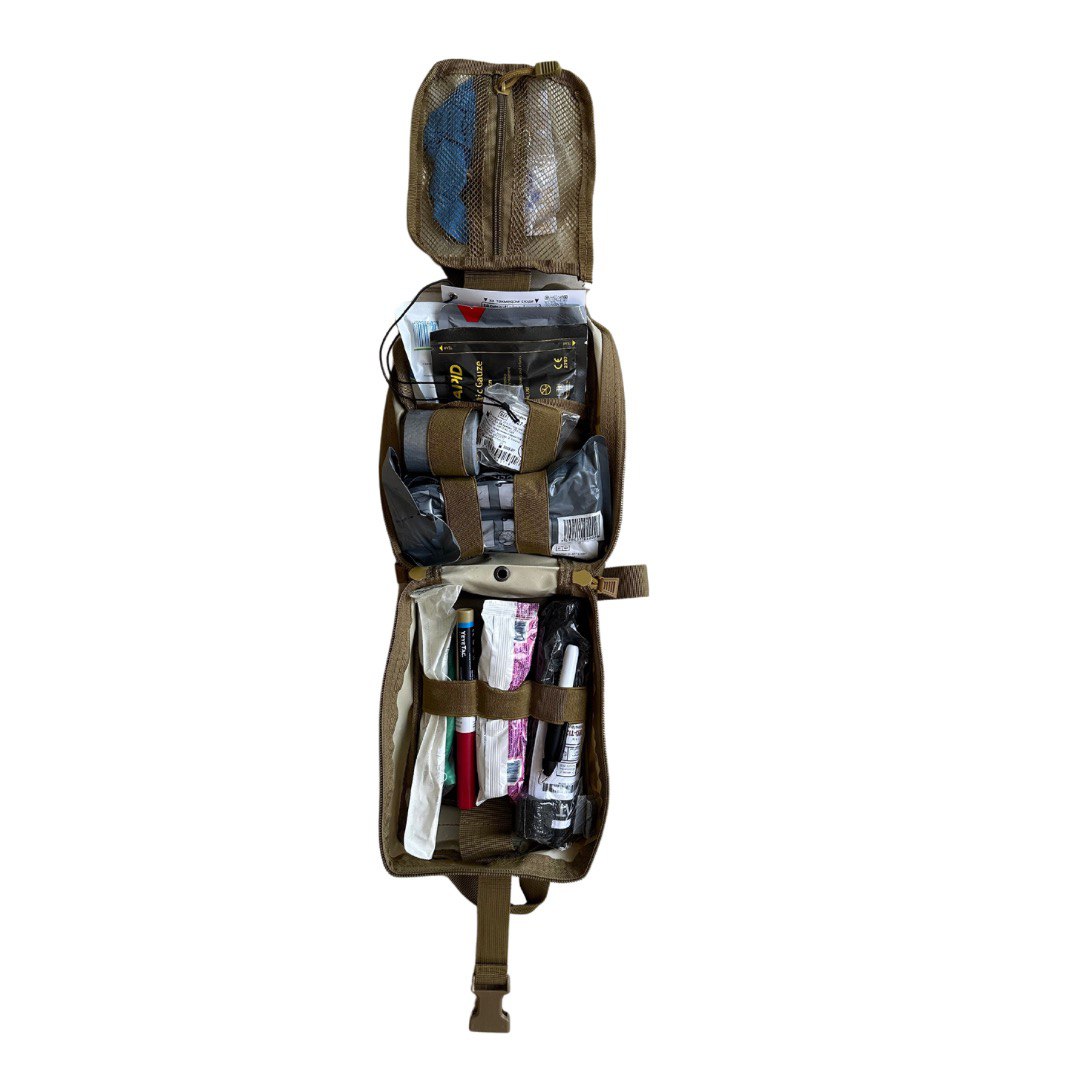
Although an individual military first aid kit may differ in composition, there are several mandatory elements. The main task of the kit is to provide immediate assistance in the field within minutes of being injured.
So what does an individual military first aid kit include? The composition is as follows:
- Nitrile medical gloves are essential for treating wounds while stopping bleeding. They help to significantly reduce the likelihood of infection.
- The tourniquet is one of the most popular medical systems used by military personnel to stop bleeding. A special material is used for its manufacture that can withstand the load. The tourniquet is applied to an injured arm or leg. The product not only withstands the load, but also retains its characteristics after getting wet. The peculiarity of this marker is that it is not erased by moisture or dirt. Thus, it can be used for writing in any environment.
- Compression bandage with a single cushion - this bandage was first used by the Israeli army, and later the US military began to use it. The included cushion provides uniform pressure over the entire area of the injury. If placed correctly, the bandage can quickly stop even heavy bleeding. The kit includes instructions to help you apply the bandage correctly.
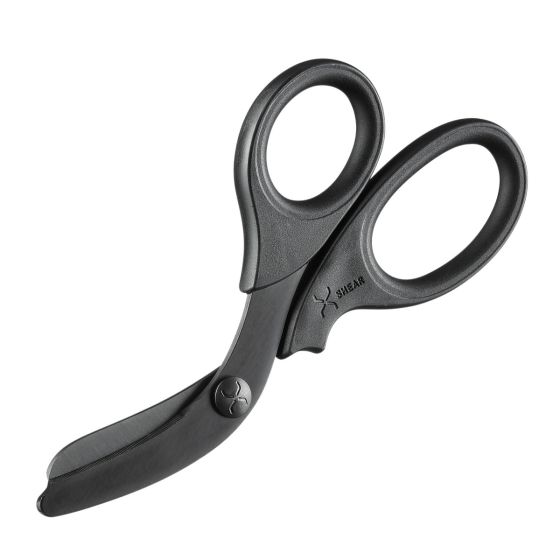
- Tactical scissors - this item is essential for gaining access to a wound. The material of the scissors allows you to quickly cut not only the military uniform, but also shoes. The scissors blades are additionally protected.
- An occlusive bandage is a product designed to help and increase the chances of survival in the event of a pneumothorax. If a soldier is injured in the chest, the body may not receive enough oxygen during breathing. This bandage or patch closes the hole due to its gel structure. The product can be used even on a dirty or wet body - its effectiveness will not be affected.
- Haemostatic bandage - this product is designed specifically to stop severe bleeding. It contains a special inert material kaolin, which has haemostatic properties.
- A thermal blanket is a special film that helps protect against overheating or hypothermia. One side of the thermal blanket has a golden coating (to protect against overheating) and the other side has a silver coating (to protect against hypothermia).
- Adhesive plaster is a product used to fix bandages or protect against cuts. The size of the plaster is 3 by 5 cm.
- A nasopharyngeal tube is a special plastic tube with a lubricant that prevents the tongue from sticking out. It is inserted through the nasal cavity, allowing the wounded person to get oxygen to the lungs.
- Decompression needle - is required during a tension pneumothorax at the stage of first aid. It is inserted into the chest to provide air access to the lungs.
- A sling cutter is a special tool that helps to quickly free a wounded person from body armour straps, nets, ropes or other equipment elements.
Now you know what a military first aid kit consists of: the set may differ, but the above elements are mandatory.
Paracetamol 500 mg tablets

This drug has three main properties: analgesic, antipyretic and mild anti-inflammatory effects. Its versatility makes it an indispensable tool in many cases. Let's consider how it can be used:
- Indications: The drug effectively relieves pain of various origins and intensity. It helps with headache, migraine, toothache, neuralgia, muscle pain (myalgia), painful menstruation (al-hodgmenorrhoea), as well as pain caused by injuries and burns. In addition, it is a reliable remedy for reducing fever in infectious and inflammatory diseases.
- Contraindications: The use of the drug should be avoided in people with hypersensitivity to its components, serious liver or kidney dysfunction, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enzyme deficiency, and blood diseases. It is also undesirable to combine its use with other hepatotoxic drugs and alcohol.
- Warnings: When prescribing this medicine, physicians should be particularly cautious with patients with impaired liver and renal function, as well as with those suffering from benign hyperbilirubinaemia. Alcohol consumption is strictly prohibited during treatment, as this significantly increases the risk of hepatotoxicity. Also, avoid combining with phenobarbital, which enhances the hepatotoxic effect of the drug.
- Dosage and methods of administration: The drug is taken orally. For adults and adolescents over 12 years of age (with a body weight of over 40 kg), a single dose of 500 to 1000 mg is recommended, with a maximum daily dose of 4 g.
- Overdose warning: Exceeding the recommended doses can lead to serious side effects such as pale skin, anorexia, nausea and vomiting. In case of an overdose of more than 10 g per day, there is a high risk of toxic hepatonecrosis, which can lead to acute liver failure.
This drug is a powerful and effective remedy for pain and fever. However, it is important to follow the recommendations for its use to avoid undesirable consequences.
Meloxicam 15 mg tablets

Meloxicam is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) known for its powerful analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties.
Like other NSAIDs, it works by inhibiting the synthesis of prostaglandins, which are key mediators of inflammation and pain. Here are the instructions for use of this medicine:
- Indications for use: Meloxicam is prescribed for the treatment of pain in injuries, as well as for the short-term treatment of symptoms of exacerbation of osteoarthritis and arthritis. Its effectiveness in reducing pain and inflammation makes it an important tool in the treatment of these diseases.
- Contraindications: However, the use of meloxicam has certain limitations. The drug is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to meloxicam or other NSAIDs. It should not be used in the active stage of gastric ulcer disease, recurrent peptic ulcer disease, and gastrointestinal bleeding. Patients who develop symptoms of asthma, nasal polyps, angioedema, or urticaria after taking acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs should also not take Meloxicam. Other contraindications include blood clotting disorders, intracranial haemorrhage, and haemorrhagic stroke. The drug is not prescribed for children under 15 years of age.
- Warnings: Particular attention should be paid to patients with inflammation of the oesophagus or stomach, as well as a history of peptic ulcer disease. These diseases should be completely cured before starting treatment with meloxicam. Patients with gastrointestinal disorders or a history of such diseases should have their condition constantly monitored. Like other NSAIDs, meloxicam can cause gastrointestinal bleeding, peptic ulcers and/or gastrointestinal rupture. Therefore, it is important to closely monitor the patient's condition during treatment.
- Dosage and route of administration: Meloxicam is taken orally with meals to help reduce the risk of gastrointestinal disorders. The recommended daily dose is 15 mg and should not be exceeded. The drug is taken with water or another drink.
In general, meloxicam is an effective treatment for pain and inflammation, but its use requires careful monitoring and compliance with all doctor's recommendations.
Gatifloxacin 400 mg tablets
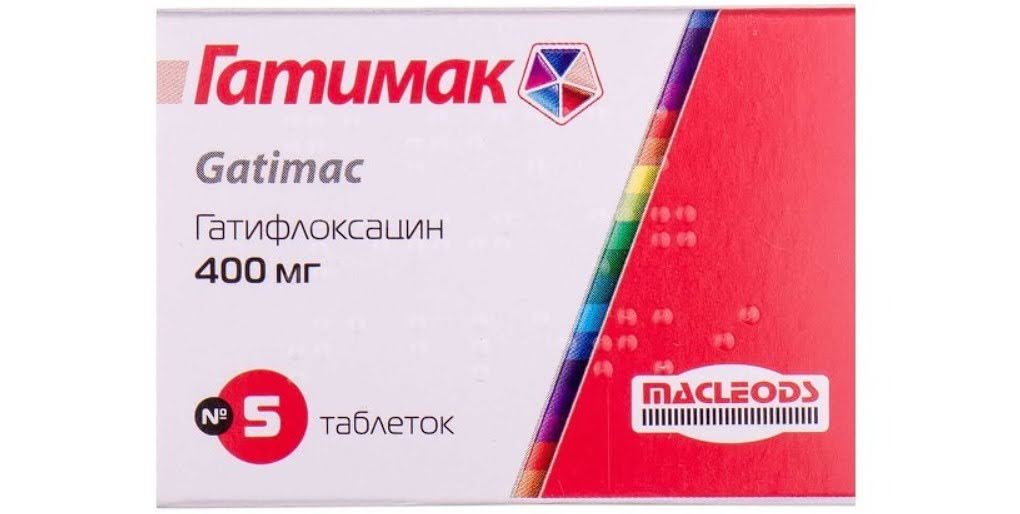
Gatifloxacin 400 mg tablets are antibacterial agents for systemic use and belong to the fluoroquinolone group. This drug is effective against a wide range of microorganisms susceptible to its action. Let's take a closer look at it:
- Indications for use. Gatifloxacin is prescribed for the treatment of various infectious and inflammatory processes, such as lower respiratory tract infections, including acute bronchitis, exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, cystic fibrosis and acute pneumonia, kidney and urinary tract infections, including acute and chronic pyelonephritis, prostatitis, cystitis and chronic urinary tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, bone and joint infections, digestive tract infections, postoperative infections;
- Contraindications. Gatifloxacin is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the drug or other fluoroquinolones, during pregnancy and lactation, and in children under 18 years of age. The drug should not be prescribed to patients with prolonged QT interval, uncorrected hypokalaemia, and those taking antiarrhythmic drugs of class IA (quinidine, novocainamide) or class III (amiodarone, sotalol).
- Warnings.Gatifloxacin should be administered with caution in central nervous system disorders, such as mental illness, epilepsy, severe cerebral atherosclerosis (risk of blood supply disorders, stroke), and in renal dysfunction, when creatinine clearance is less than 40 ml/min. In such cases, it is necessary to monitor the drug concentration in the blood plasma.
- Dosage and route of administration. For persons over 18 years of age in acute and complicated bronchitis, pneumonia, skin and subcutaneous tissue infections, acute pyelonephritis and complicated urinary tract infections, the dose is 400 mg once daily or 200 mg twice daily for 7-10 days.
Gatifloxacin is an effective antibacterial agent that helps fight a wide range of infections, but its use requires a careful approach and compliance with all doctor's recommendations.
What not to put in the Pill pack

When putting together a military first aid kit, it is important to know what to include. It is equally important to understand which items are best left out. Military experts advise against certain components that can undermine the effectiveness of your first aid kit.
First of all, you should avoid powerful painkillers. They may provide some relief, but their benefits are small compared to the risks involved. During injuries, the body needs precise dose control, which can be difficult in the field. An overdose can have serious consequences, including death.
It is also not recommended to use haemostatics in powder form. Their use can be inconvenient, especially in bad weather. Hemostatics in the form of bandages or capsules are much more practical and effective in such situations.
The Esmarch tourniquet, once considered a reliable means of stopping bleeding, has lost popularity in favour of modern alternatives. It is inconvenient to use in the field, and the material easily tears under load. Modern certified tourniquets recommended by military and medical institutions are considered better alternatives.
Thus, modern tactical first aid kits are ahead of their predecessors. Even in the case of serious injuries, a compact set of medicines allows for effective first aid. In addition, the components of the first aid kit are designed to be easily used by individual soldiers, enabling them to provide emergency medical care at the right time.



