Providing first aid for injuries
Content
- What is Medical Assistance?
- Types of Injuries
- Principles and Algorithm of Actions in Providing Medical Assistance
- First Aid for Bleeding
- First Aid for Fractures
- First Aid for Wounds
- Contents of a First Aid Kit for Home Medical Assistance
- Tips for Providing First Aid
- FAQ
- How to prevent fractures?
- What is a bruise?
- How to properly position a victim for first aid?

First aid is the provision of basic medical care aimed at saving lives, reducing the suffering of the injured in emergency situations, and preventing potential complications.
This type of assistance is usually provided by medical professionals, but emergency medical services may not always arrive at the scene on time. Therefore, the ability of any of us to provide necessary aid to the injured before the arrival of professionals can play a crucial role in saving a person's life.
What is Medical Assistance?
Providing first aid means performing basic measures to preserve life, reduce the suffering of the injured from an emergency situation, and prevent potential complications.
Injuries can have various natures. The most significant are combined injuries to several organs. Less dangerous but serious ones include various types of wounds, burns, fractures of limb bones, spine, pelvis, dislocations in large joints.
Less severe injuries include minor injuries, bruises, damage to the ligamentous apparatus. It is also important to consider psychological trauma, such as post-traumatic stress disorder after military actions. The ability to provide first aid to the injured before the arrival of emergency medical services is crucial for the rescue mission.
Timely medical assistance in case of injury increases the chances of a positive prognosis for the injured person, so it is important for everyone to have the knowledge and skills to provide it properly and promptly.
Types of Injuries
The following types of injuries are distinguished:
- Serious massive trauma, such as combined fractures and traumatic shock resulting from a fall from a height.
- Injuries, such as a fracture of the shin after a fall on skis.
- Psychological trauma, for example, post-traumatic stress disorder after military events.
Injuries are classified according to the circumstances in which they occurred and are divided into intentional and accidental.
Intentional injuries or wounds include various forms of violence or actions in conditions of war and may also result from self-harm, such as suicide. Accidental injuries may result from falls, car accidents, lightning strikes, and similar circumstances.
Principles and Algorithm of Actions in Providing Medical Assistance
This section will cover the basic principles, rules of providing first aid, and clear action algorithms that need to be considered when providing medical assistance.
The Ministry of Health recommends applying the following action algorithms in case of injury:
- Start by ensuring safety at the scene - both yours and that of the injured persons.
- Assess the condition of the injured person (check breathing, pulse, consciousness).
- Call the emergency medical service and, if necessary, other emergency services (police, fire brigade, gas service, etc.).
- Check for critical bleeding, and if present, stop it immediately.
- Ensure the openness of the airways.
- If there are no signs of life or bleeding after checking, perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
- If there are no suspicions of spinal injuries and pelvic fractures, and if resuscitation (if necessary) was successful, transfer the injured person to a stable position. For example, on the side, facing you, with the head elevated and the knee bent.
- Do not leave the injured person unattended until the arrival of medical services.
First Aid for Bleeding
With every injury, it is important to pay attention to the presence of bleeding first. Blood loss can suddenly worsen the condition of the injured person and lead to shock. It is also important to consider the general condition of the body and not to overlook other possible threats, such as the possibility of a fracture of the cervical spine.
During contact with bleeding, always use personal protective equipment (rubber gloves, goggles) to avoid the risk of infection, such as HIV or viral hepatitis. When attempting to stop bleeding, it is important to seek qualified help immediately by calling the emergency medical service.
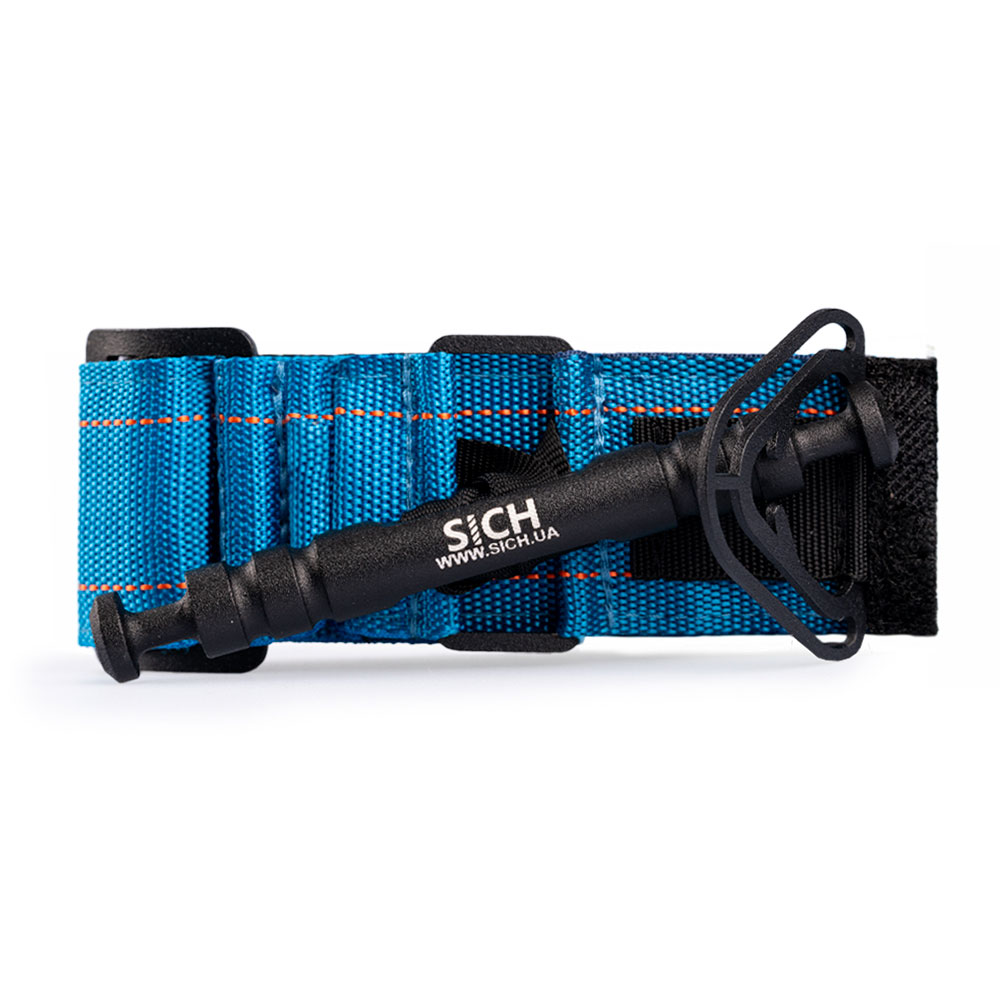
An effective way to stop bleeding from a wound is direct pressure. Apply a sterile bandage and apply strong pressure to the injured area. If the bleeding is arterial, apply a tourniquet above the site of injury and record the time the tourniquet was applied.
If bleeding is in multiple locations, prioritize attention to the more massive bleeding, seeking assistance to compress other areas while you work with the initial injuries.
A quick makeshift tourniquet can be created from fabric and an object resembling a stick, rotating it to increase pressure on the tissues.
There are also ready-made tourniquets:
- Classic Esmarch tourniquet (long rubber band with a clip).
- Modern and convenient C-A-T Tourniquet, which can be applied independently.
When applying a tourniquet, perform the following actions:
- Put on personal protective equipment.
- Place the tourniquet about 5 cm above the wound (in case of arterial bleeding).
- Tighten it until the bleeding stops.
- Record the time of application.
- Call an ambulance.
Stay with the injured person until medical help arrives. If more than 30 minutes have passed and the blood loss is not life-threatening, slightly loosen the tourniquet for a few minutes to restore blood flow, then reapply it. You can learn more about how to use a tourniquet in our article: "How to Properly Use a Tourniquet?"
Important: Prolonged constriction can cause hypoxia and the need for further amputation, so it is important to transport the injured person to a surgeon as quickly as possible.
First Aid for Fractures
A fracture is a bone injury accompanied by a disruption of its integrity. Traumatic fractures are divided into open and closed. In the case of an open fracture, the injury is easy to notice. A closed fracture is not always obvious, so it is important to first determine the type of injury the injured person sustained. So, to provide first aid for fractures, you should know:
Signs of a limb fracture:
- Possible sound of bone fracture;
- Intense pain;
- Deformation of the limb (change in shape);
- Swelling, bruising, or pain around the injury;
- Numbness and tingling;
- Restricted movement of the limb;
- Increased pain with movement;
- Possible protrusion of the bone from the wound in an open fracture.
Since fractures can be accompanied by severe pain leading to shock, it is recommended to provide the injured person with analgesics.
Head injuries are always serious types of injuries.
Signs of a head injury and traumatic brain injury include:
- Loss of consciousness;
- Impaired coordination and balance;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Seizures;
- Headache;
- Memory loss;
- Confusion.
When preparing the injured person for transport to a medical facility, it is important to stabilize the head and neck (using a neck brace or hands) to prevent further injury.
Strains occur when a joint is pushed beyond its natural range of motion due to improper movements or excessive stress. Strains are often indicated by pain, bruising, and swelling, but an X-ray is needed for an accurate diagnosis of a fracture.
Fractures and injuries to the pelvic bones and joints are complex. In these cases, as well as in spinal and neck injuries, timely medical assistance can be crucial for the further condition of the injured person. It is important to ensure the transportation of the injured person to a medical facility in an immobilized state.
First Aid for Wounds
For any skin and deep tissue injury, it is important to apply wound treatment with iodine or alcohol solution. Washing the wound with water or disinfectant solution is prohibited. After treatment, apply an aseptic dressing to protect against contamination and prevent infection. It is important to adhere to the following wound treatment rules:
- Wash your hands before treating the wound or wipe them with alcohol if there is no water nearby.
- For small wounds around the treated skin, apply iodine or hydrogen peroxide, then apply a plaster or medical adhesive BF-6.
- Do not remove foreign bodies or dirt from the wound to avoid damaging blood vessels and bleeding.
- Wipe the skin around the wound from the edges to the center using alcohol, iodine solution, or gasoline. Avoid pouring iodine into the wound.
- From a bandage or individual packet, create a napkin covering the entire wound and attach it to the wound surface using adhesive plaster.
- If internal organs, brain, or tendons are visible, cover the wound with sterile material or apply a careful sterile dressing.
Protect the wound from contamination by observing the treatment rules, which will help avoid complications and promote rapid healing.
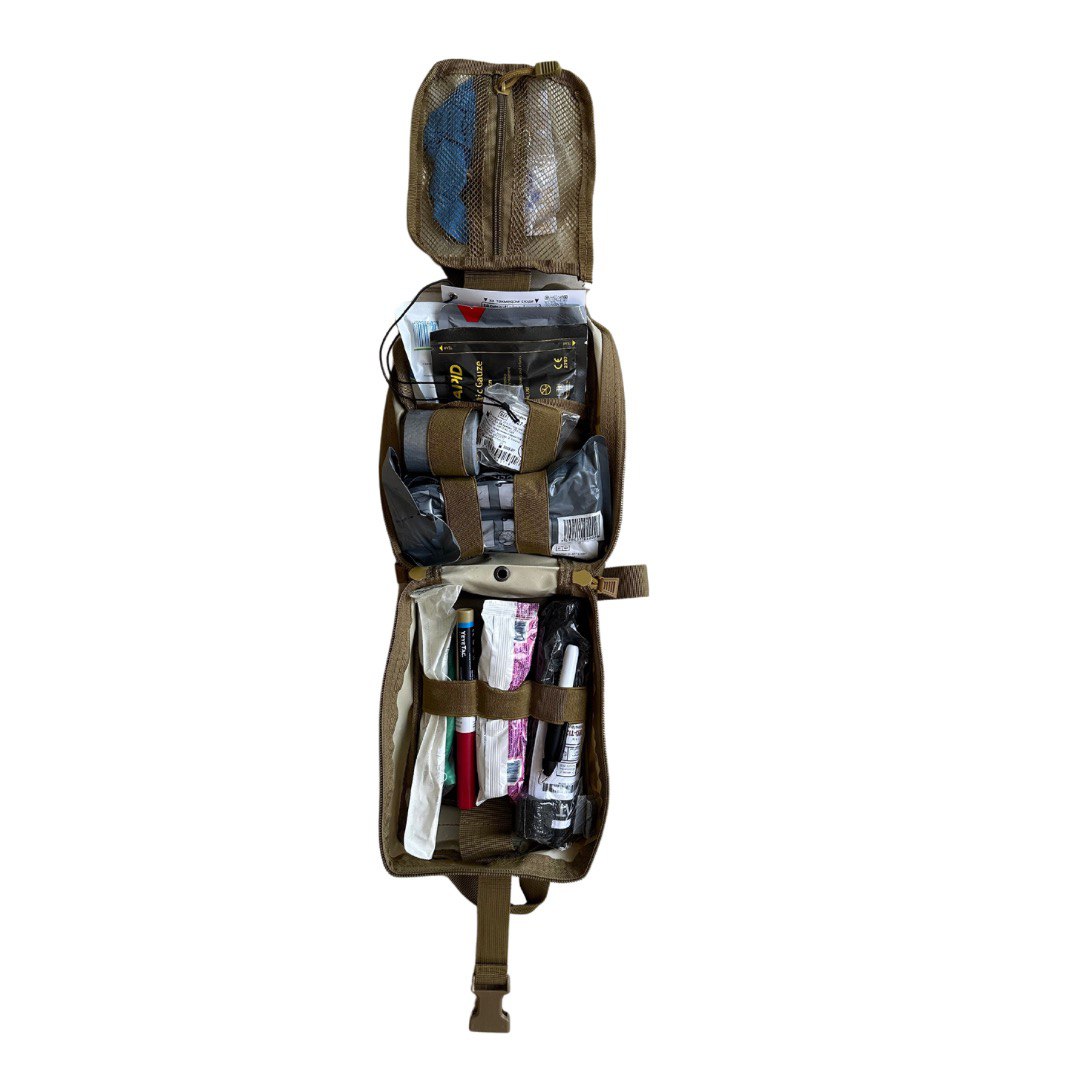
Contents of a First Aid Kit for Home Medical Assistance
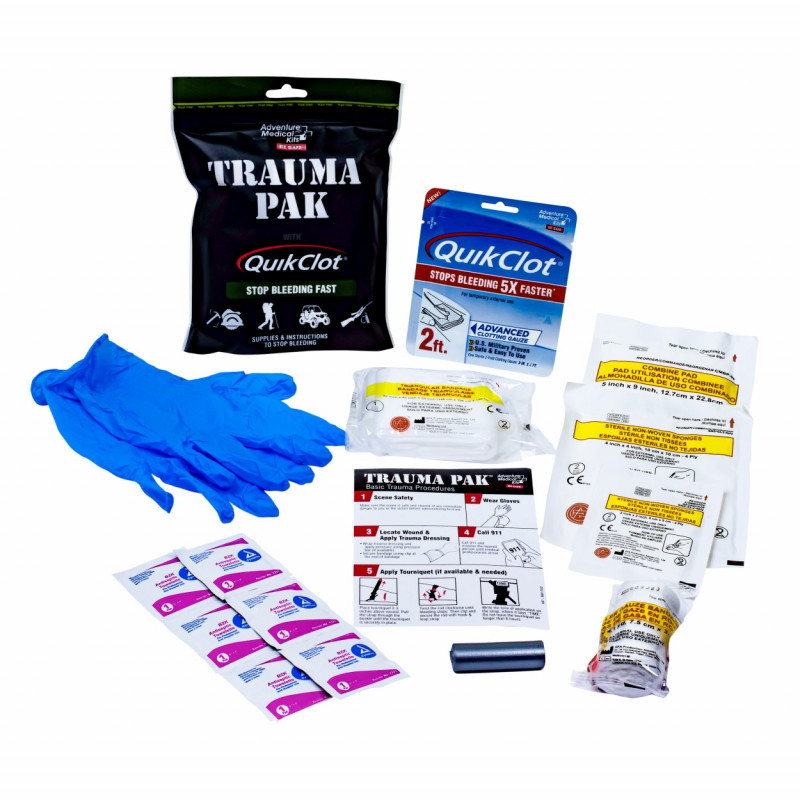
Today, every person from Ukraine should have a properly assembled first aid kit, which can be extremely useful in dangerous situations before medical assistance arrives. It is much better to assemble a first aid kit yourself, taking into account personal health characteristics, than to buy a ready-made kit that may be less adapted to your needs. The contents of the first aid kit can be divided into two groups: medicines and medical materials, such as dressing tools and other auxiliary means.
The first aid kit must include:
- Scissors.
- Tweezers.
- Safety pin.
- Disposable gloves.
- Tourniquet.
- Disposable syringes.
- Bandage and cotton wool.
- Individual dressing package.
- Adhesive plaster.
- Antiseptic wipes.
- Fixing bandage 50 X 50 cm.
- Burn dressing.
Medications in an emergency first aid kit
- 5% Iodine solution
- Antiseptic
- Antibacterial ointment
- Burn remedies (Betadine, Panthenol, Aekol)
- Oral rehydration solutions (Rehydron, Regisol, Ionika)
- Enterosorbents (Atoksyil gel, Enterosgel, Polysorb, Sorbex)
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drugs
- Antihistamine drugs (Allegra, Zyrtec, Xitax, Claritin, Erius, Edem)
- Cardiovascular system medications
- Iodine tablets
- Hormonal medications
- Antidiarrheal drugs (Loperamide, Imodium, Smecta)
- Sedative drugs (Valerian, Persen, and Novo-Passit)
Tips for Providing First Aid
The main tips for providing first aid are:
- Ensure safety: Before providing assistance, make sure the environment is safe for both you and the victim. Avoid risks if the situation may threaten your safety.
- Call for help: Immediately call emergency medical assistance or other necessary services (fire department, police, etc.) if the situation requires professional help.
- Assess the victim's condition: Determine if the victim is conscious, breathing normally, showing signs of bleeding, or has visible injuries. This will help you understand what assistance they need.
- Stop the bleeding: If there is bleeding, try to stop it by applying direct pressure to the wound or using suitable materials at hand.
- Ensure airway access: In cases where the victim is not breathing, start resuscitation measures. Check for breathing, start artificial respiration, and perform chest compressions.
- Apply dressings and bandages: Use aseptic methods when applying dressings to wounds. Cover wounds to prevent infection and contamination.
- Stay calm and communicate: It is important to remain calm and confident. Talk to the victim, provide support, and reassure them.
- Do not leave unattended: After providing first aid, stay with the victim until professional medical help arrives.
- Master the basics of first aid: Knowledge of basic first aid methods can save lives. It is recommended to take a special first aid training course to be prepared to act in dangerous situations.
- Do not be guided by fear: Even in extreme situations, try to remain rational and focused. The actions you take can help save lives.
- Remember that properly administered first aid can significantly alleviate the victim's condition and help save their life until professional medical services arrive.
FAQ
How to prevent fractures?
Of course, it is impossible to completely avoid fractures, but you can increase bone strength by eating properly, consuming foods rich in vitamin D and calcium. It is also important to regularly engage in moderate physical exercises such as swimming or walking and ensure that weight is within normal limits.
What is a bruise?
Bruise is soft tissues or internal organs suffer. We feel pain, the bruised area may swell, subcutaneous vessel rupture may occur, and a hematoma may form. When muscles of the arms or legs are bruised, stiffness and limited movement may be observed. Much more dangerous are contusions of internal organs. They can significantly disrupt their function and even lead to death.
How to properly position a victim for first aid?
You need to remove the victim from the water, place them so that their head is below, for example, the abdomen on your knee, clear the airways of various foreign objects. If you notice that the victim is not breathing and/or has no pulse, immediately start indirect heart massage and artificial respiration.


