First aid in case of respiratory arrest
Content
- Causes of respiratory arrest
- Symptoms that indicate respiratory failure
- Resuscitation actions
- How to perform artificial respiration
- How to perform indirect heart massage
- Conclusion

First aid for cardiac arrest is critical to a successful outcome. When the heart stops working, the brain remains alive for only a short period of time.
Delaying treatment can lead to irreversible changes that may prove fatal. It is important to provide the brain with the necessary access to oxygen by providing first aid in case of respiratory arrest. Despite this, the level of blood circulation remains insufficient, which can complicate the situation.
Causes of respiratory arrest

The current understanding of respiratory arrest classifies it as an extremely dangerous condition that requires immediate action. The body can only survive without oxygen for a limited time - approximately 5-6 minutes.
Delay in providing assistance can lead to uncontrollable changes that can be fatal for the victim.
Therefore, any suspicion of respiratory arrest should be taken as a warning signal for immediate resuscitation. Knowledge of these factors is important for timely intervention and effective medical care.
Some of them are shown in the table below:
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Foreign objects or fluids in the throat | Even small objects entering the airways can block normal breathing and lead to respiratory arrest. |
| Swelling or spasms of the throat | Sensation of throat constriction or swelling can obstruct airflow and trigger respiratory arrest. |
| Shock due to trauma | Severe stress or injury can induce a shock state, which may result in respiratory arrest due to organ dysfunction. |
| Airway obstruction during unconsciousness | Unconsciousness can lead to airway obstruction by the tongue, resulting in respiratory arrest. |
| Trauma to respiratory organs | Injuries disrupting the integrity of the airways and lungs can cause respiratory arrest due to impaired function. |
| Inhalation of toxic fumes | Inhaling toxic substances can lead to paralysis of respiratory centers in the brain, resulting in respiratory arrest. |
| Damage to the respiratory center | Damage to the respiratory center due to electric shock, head injury, or ingestion of potent drugs can disrupt normal breathing processes. |
Symptoms that indicate respiratory failure
When a person stops breathing, there are several signs. You can put your hands on the chest or place your cheek in front of the victim's mouth and nose.
The chest does not rise, and there is no breathing through the nose or mouth. Control is carried out for a maximum of 10 seconds.
If breathing is not detected, immediately dial the emergency number and start resuscitation. Providing first aid in case of respiratory arrest is no less important than transporting the patient to a medical facility as soon as possible.
This assistance should be provided without delay in the event of:
- Wheezing of the victim.
- Sudden pallor of the skin to a cyanotic tint around the lips and tips of the ears.
- Absence of rhythmic movements of the abdominal muscles or chest accompanied by inhalation/exhalation.
- No movement of air entering and leaving the airways.
- Absence of inhalation and exhalation sounds while bending over the victim.
Any delay in providing assistance with these symptoms can be fatal.
Resuscitation actions
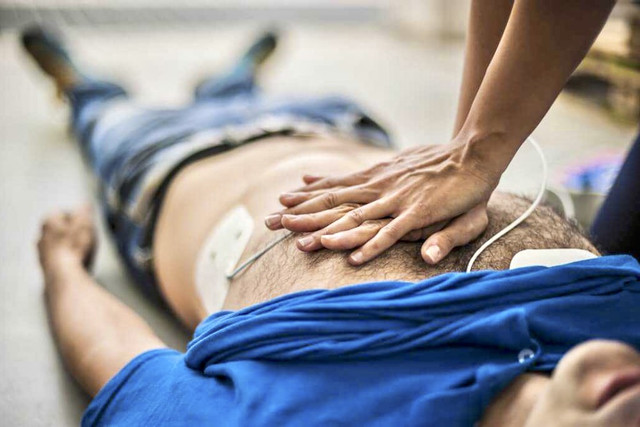
First aid in case of respiratory arrest is a critical step, as is rapid transport to a medical facility.
It is important to take the following steps immediately:
- Place the victim on a hard surface.
- Undo the collar, buttons, and belt.
- Clean the oral cavity from foreign objects.
- Place the victim on his/her left side and kneel down next to him/her.
- Check for a pulse and make sure there is no breathing.
- Perform artificial respiration and indirect heart massage.
- Place a bundle of clothes under the victim's shoulders, tilt the head back and open the mouth.
- Cover the mouth with a piece of thin cloth.
- Breathe air into the victim's mouth, holding the victim's nose.
- Take several full breaths, opening the nose and freeing the mouth.
- Make 5 sharp presses on the sternum.
These steps should be continued until the victim begins to breathe on their own and regains consciousness. The speed and accuracy of each step is critical, as every second counts.
If you need to resuscitate a child, you need to cover the child's respiratory organs with your lips and perform indirect heart massage.
For a preschool child, two fingers are used, and for a schoolchild, one hand is used. If you know about possible injuries to the spine or head, you should refrain from moving the victim.
If you stop breathing in a dream, you should immediately seek qualified medical help. It is desirable to have knowledge of the correct closed heart massage to provide first aid yourself.
If resuscitation measures are carried out by two people, one person performs 5 presses on the chest, and the other person gives vigorous breaths of air to the victim.
These actions are repeated 12 times in 60 seconds. In case of self-care, all actions should be performed even faster: 15 presses in 12 seconds, 2 vigorous breaths in 3 seconds.
In a minute, 8 full breaths and 60 presses on the sternum should be performed.
How to perform artificial respiration

If the victim has lost consciousness and does not respond to your actions, and you do not notice any chest movement within 10 seconds, which indicates that there is no breathing, you should first call an ambulance.
If there are other people with you, ask one of them to do it to save you the time needed to provide medical assistance.
Until the professional medical team arrives, follow this sequence of actions:
- Place the victim on a hard, flat surface.
- Undo the collar, buttons and belt to free the throat and upper chest from clothing.
- Free the mouth from water, algae and other foreign objects.
- Kneel on the victim's left side.
- Check for a pulse at the wrist or neck artery.
- Place a roller or bundle of clothing under the victim's shoulders.
- Start CPR by covering the mouth with a piece of thin cloth.
- Breathe air into the victim's mouth by pinching the nose (5 breaths).
- Open the nose and count to five (5 exhalations).
- During CPR, it is recommended to perform indirect heart massage by pressing the chest with your hand in sync with the breaths.
- If the victim has fractures of the ribs or spine, it is better to limit the ventilation to the lungs.
- If you suspect a head injury, do not move the victim.
- When providing first aid in the event of respiratory arrest, one person can perform cardiac massage by pressing the chest area with both hands 5 times in a row, while the other person provides vigorous breaths of air into the victim's lungs.
- A total of 12 repetitions should be performed within 1 minute.
For preschool children, heart massage is performed with two fingers, and for schoolchildren, with one hand. If a child needs resuscitation, he or she can be resuscitated by placing his or her lips around the child's respiratory system.
All these actions should be performed until the victim starts breathing on their own and regains consciousness. Providing assistance should be consistent and very fast, as every second counts.
If you are performing the resuscitation yourself, you should do it even faster: 15 compressions on the sternum for 12 seconds, followed by 2 vigorous exhalations in 3 seconds, so that 60 compressions and 8 resuscitations are performed in 1 minute.
The Ambu bag can facilitate and speed up the process of restoring breathing to the victim.
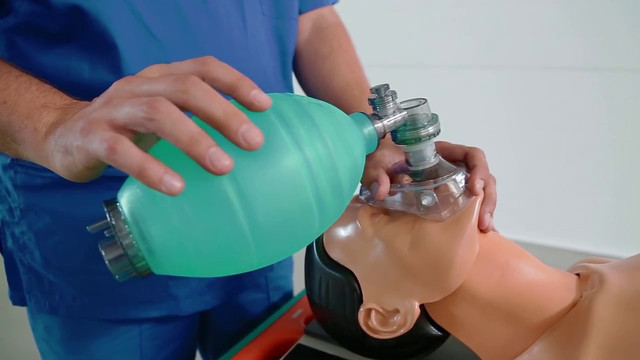
It consists of a cavity filled with air and a silicone mask used to manually ventilate the lungs by compressing the bag, and the airways are filled with the required amount of oxygen.
How to perform indirect heart massage
If there is no pulse and there is no breathing, indirect cardiac massage should be performed.
This type of massage, also known as chest compression, involves compressing the heart muscles between the chest and spine to maintain circulation in the event of cardiac arrest.
It is one of the primary procedures in the intensive care unit.
It is important to remember that indirect heart massage should not be performed if the victim has a pulse.
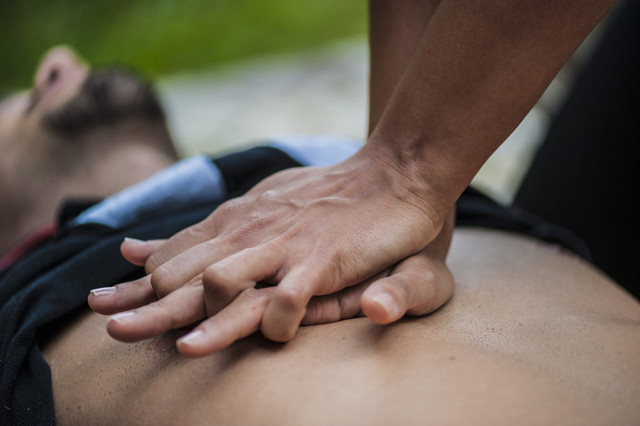
Here is the technique of indirect heart massage:
- Place the victim on a flat, hard surface. Chest compressions should only be performed on a hard surface, as they should not be performed on a bed or other soft surfaces.
- Locate the victim's xiphoid process. This is the shortest and narrowest part of the sternum, its highest point.
- Measure 2-4 cm upwards from the xiphoid process - this will be the point of compression.
- Place the base of your palm on the compression point. Your thumb should point either to the chin or to the victim's abdomen, depending on the position of your face.
- Place the second palm over the first. The pressure should be applied with the base of the palm, without direct contact with the victim's chest.
- Perform rhythmic, deep, vertical chest compressions using the weight of your upper body. The frequency is 100-110 strokes per minute, with a 3-4 cm deflection of the chest.
In children, heart massage is performed with the index and middle fingers of one hand. In adolescents, it is enough to use the palm of one hand.
If artificial lung ventilation is performed simultaneously with indirect heart massage, then every two breaths alternate with 15 chest compressions.
Conclusion
In cases of respiratory and pulse arrest, first aid is crucial.
Indirect heart massage, along with artificial lung ventilation, can save the victim's life.
It is important to perform all the necessary procedures skilfully and quickly, taking into account the victim's age and condition.
Perfect training and the ability to provide effective medical care in critical situations can make a significant contribution to saving a person's life.